

- #CARBON ELECTRON CONFIGURATION STANDARD FORM FULL#
- #CARBON ELECTRON CONFIGURATION STANDARD FORM PLUS#
This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.įurther, we at provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion.īalbharati solutions for Mathematics Science 8th Standard Maharashtra State Board Maharashtra State Board 5 (Inside the Atom) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations.

Thus, the columns of the periodic table represent the potential shared state of these elements' outer electron shells that is responsible for their similar chemical has the Maharashtra State Board Mathematics Science 8th Standard Maharashtra State Board Maharashtra State Board solutions in a manner that help students When an atom gains an electron to become a negatively-charged ion this is indicated by a minus sign after the element symbol for example, \(F^-\). Group 17 elements, including fluorine and chlorine, have seven electrons in their outermost shells they tend to fill this shell by gaining an electron from other atoms, making them negatively-charged ions.
#CARBON ELECTRON CONFIGURATION STANDARD FORM PLUS#
When an atom loses an electron to become a positively-charged ion, this is indicated by a plus sign after the element symbol for example, Na +. As a result of losing a negatively-charged electron, they become positively-charged ions. This means that they can achieve a stable configuration and a filled outer shell by donating or losing an electron. In comparison, the group 1 elements, including hydrogen (H), lithium (Li), and sodium (Na), all have one electron in their outermost shells. Their non-reactivity has resulted in their being named the inert gases (or noble gases). As shown in, the group 18 atoms helium (He), neon (Ne), and argon (Ar) all have filled outer electron shells, making it unnecessary for them to gain or lose electrons to attain stability they are highly stable as single atoms. The periodic table is arranged in columns and rows based on the number of electrons and where these electrons are located, providing a tool to understand how electrons are distributed in the outer shell of an atom.
#CARBON ELECTRON CONFIGURATION STANDARD FORM FULL#
Elements in other groups have partially-filled valence shells and gain or lose electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration.Īn atom may gain or lose electrons to achieve a full valence shell, the most stable electron configuration. A full valence shell is the most stable electron configuration.
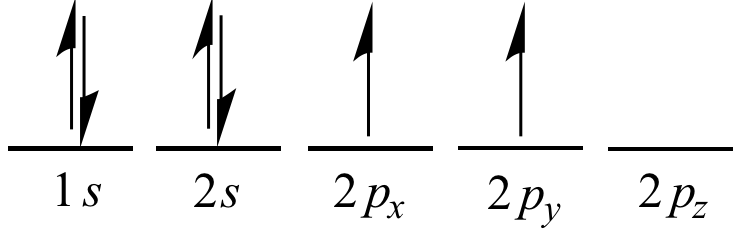
Group 18 elements (helium, neon, and argon are shown) have a full outer, or valence, shell. \):īohr diagrams indicate how many electrons fill each principal shell.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
